Setting up a JogAmp project in your favorite IDE
These instructions assume that you've created a project in your favorite IDE, and now you want your project to be able to use a JogAmp library like JOGL, JOCL, JOAL, or GlueGen. We use JOGL as an example below, but these instructions work equally well for any other JogAmp library.
Download a JogAmp library
If you haven't done so already, download and extract the JogAmp library you want to use. For example, to download and extract JOGL, see the instructions at Downloading and installing JOGL.
To use a JogAmp library you'll have to do two things:
- Add its JAR files to the Java classpath
- Add its native libraries in one of two ways:
- Either place its native JAR files in the same directory as the library JAR files
- Or add its native libraries to the Java library path
Each IDE has a slightly different way to do these things, as we show below. Using the native JAR files is usually slightly easier than using the native library files directly, and native JARs make it possible for all platforms' libraries to coexist in one project, so this is the recommended method.
Please note that all JogAmp libraries depend on the GlueGen runtime libraries. These are included in every JogAmp library for convenience, but are only required once in the classpath and library path of your project.
Eclipse IDE
Create a user library
You can make your new Eclipse project depend directly on all the JARs and native libraries, but it's inconvenient to do that every time you create a new project. Creating a user library bundles all the files together so you can include them in one step.
- Click "Window > Preferences", then select "Java > Build Path > User Libraries" on the left.
- Click the "New..." button, type "JOGL" for the library name, and click "OK".
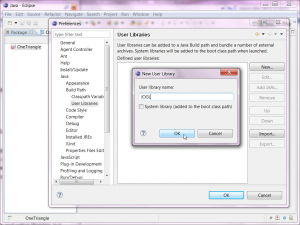
- Click the "Add JARs..." button, navigate to the directory where you've stored the JARs, select them, then click "Open".
- Expand each JAR in the list
- Double-click "Source attachment", type the module's source zip name, (e.g. jogl-java-src.zip for the JAR file jogl.all.jar), and click "OK".
- If you're using native JAR files:
- Make sure the gluegen-rt-natives-*-*.jar and jogl-all-natives-*-*.jar files for each platform you want to run on are in the same directory as the other JAR files. The native JAR files don't need to be added to the classpath.
- Otherwise, if you're using native library files:
- Double-click "Native library location", type the directory where native library files are stored, and click "OK".
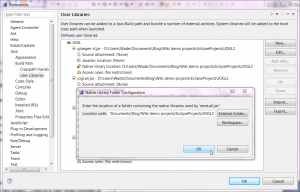
- Click "OK" to exit Preferences dialog.
Add the user library to your project's dependencies
- Right-click your project in the Package Explorer and clock "Properties".
- Select "Java Build Path" and click the "Libraries" tab.
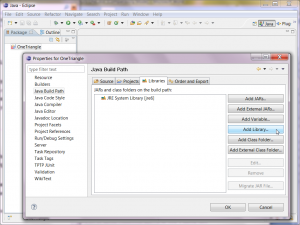
- Click "Add Library...", select "User Library", click "Next", check "JOGL", and click "Finish".

- Click "OK" to dismiss the Properties dialog.
That's it! You can now use the library in your project.
IntelliJ IDEA
Add a library dependency to your project
- Click "File > Project Structure".
- Select "Modules" on the left, then click the "Dependencies" tab on the right.
- Click the "Add..." button, then click "Library...".
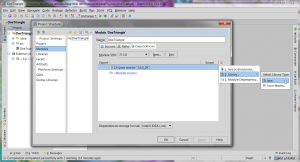
Add library - Type "JOGL" as the library name.
- Click "Attach JAR Directories...", navigate to the directory where you extracted the JARs and click "OK".
- Click "OK" to dismiss the Configure Library dialog.
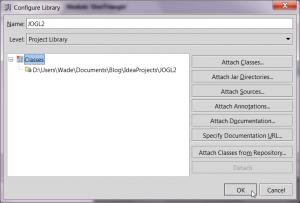
Configure library - Click "OK" to dismiss the Project Structure dialog. The external libraries in your project should now look like this.
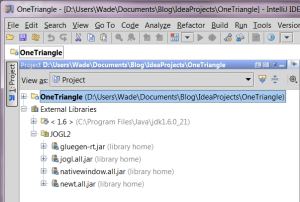
External libraries
- If you're using native JAR files:
- Make sure the gluegen-rt-natives-*-*.jar and jogl-all-natives-*-*.jar files for each platform you want to run on are in the same directory as the other JAR files. The native JAR files don't need to be added to the classpath.
- Otherwise, if you're using native library files:
That's it! You can now use the library in your project.
NetBeans IDE
Create a library and add it to your project
- Right-click your project and click "Properties".
- Select "Libraries" on the left and click "Add Library...".
- Click the "Create" button, then type "JOGL" for the library name and click "OK".

Create library - Click "Add JAR/Folder...", then navigate to the directory you extracted the JAR files, select them and click "Add JAR/Folder".
- Click "OK" to dismiss the Customize Library dialog.
- Click "Add Library" to dismiss the Add Library dialog.

Add library - Click "OK" to dismiss the Project Properties dialog. The libraries in your project should look like this.
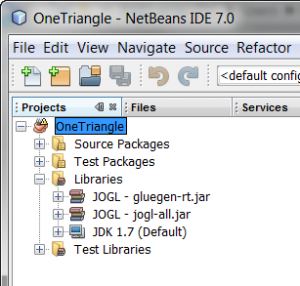
Libraries in project
- If you're using native JAR files:
- Make sure the gluegen-rt-natives-*-*.jar and jogl-all-natives-*-*.jar files for each platform you want to run on are in the same directory as the other JAR files. The native JAR files don't need to be added to the classpath.
- Otherwise, if you're using native library files:
- Click "Run > Set Project Configuration > Customize...". Select "Run" on the left if it isn't selected already.
- Type -Djava.library.path=your/path/to/native/library/files in the "VM Options" box.
- NOTE: If the library path has spaces in it, you must put quotes around it (at least on Windows) or you may get an odd NoClassDefFoundError when you try to run.
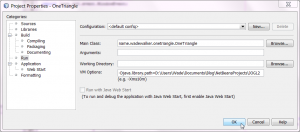
Native library path - Click "OK" to dismiss the Project Properties dialog.
That's it! You can now use the library in your project.
vi and other text editors
Create your project with the editor of your choice
- For example, to open vi, simply type vi and press <return>.
- Type all your code, then save it.
Compile and run your project from the command line
- We assume your JOGL JAR files are in a directory called jar. If you're using native JARs, we assume they're also in the jar directory. If you're using native library files, we assume they're in a directory called lib.
- First compile your program. We assume all your code is in a single file called name/someone/MyProject.java.
- Windows: Type javac -classpath "jar\gluegen-rt.jar;jar\jogl.all.jar" name\someone\MyProject.java
- Linux/MacOS X: Type javac -classpath "jar/gluegen-rt.jar:jar/jogl.all.jar" name/someone/MyProject.java
- Then run your project. We assume your main class is name.someone.MyProject. If you're using native JARs:
- Windows: Type java -classpath "jar\gluegen-rt.jar;jar\jogl.all.jar;." name.someone.MyProject
- Linux/MacOS X: Type java -classpath "jar/gluegen-rt.jar:jar/jogl.all.jar:." name.someone.MyProject
- If you're using native library files:
- Windows: Type java -classpath "jar\gluegen-rt.jar;jar\jogl.all.jar;." -Djava.library.path=lib name.someone.MyProject
- Linux/MacOS X: Type java -classpath "jar/gluegen-rt.jar:jar/jogl.all.jar:." -Djava.library.path=lib name.someone.MyProject
That's it! You can now use the library in your project.